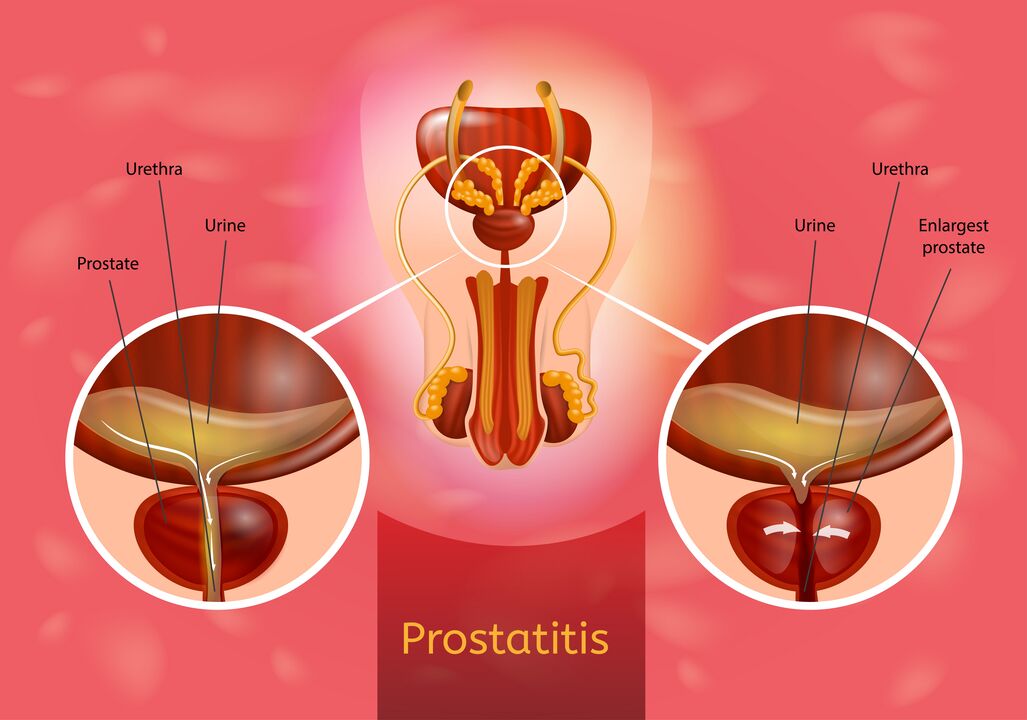
Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate (prostate) that develops due to inflammatory changes.According to statistics, the prevalence of the disease reaches 35-50%, and is found in men aged 20-40.
type
Distinguish 4 forms of prostatitis:
- Acute (bacterial);
- Chronic bacteria;
- Chronic non-bacterial;
- Asymptomatic chronicity.
Acute prostatitis is very rare due to the rapid process of the inflammatory process and the direct transition to the chronic stage (error improvement).
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, otherwise known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, may be inflammatory (present in the urine and high in leukocytes that ejaculate), rather than inflammatory.
reason
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis are pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi).Most commonly, the root causes of inflammation are:
- E. coli;
- Streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- proteus;
- Claybosella;
- Fake stick;
- Pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases (Chlamydia, Mycobacterium, Gonococcal, Trichomonas, Cytomegavirus, etc.).
Most microorganisms are in the intestine, on the skin, but, entering prostate tissue, they cause an inflammatory process.Usually, the cause of the disease is not a pathogen, but a connection between several types of microorganisms.
The development of chronic prostatitis can cause the following factors:
- Urinary system accompanied by diseases (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- A sedentary lifestyle ("sitting" work);
- Trends of constipation;
- Defensive measures to weaken the body;
- Injuried;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- alcoholism and smoking;
- Random sex;
- Irregular sex life (long-term abstinence);
- Interrupted sexual intercourse;
- Irregular emptying of the bladder;
- Dissatisfied sexual desire;
- Chronic stress;
- Low temperature;
- Fever teeth and other sources of chronic infections (e.g., chronic tonsillitis).
Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is a very sinister disease."Capturing" it is very difficult because first, the process quickly becomes chronic, and secondly, most patients prefer the manifestations of "sinking" the house's acute prostatitis.In advanced cases with erectile dysfunction and other consequences, patients with prostatitis are usually targeted by doctors.
The acute form of the disease is performed in the context:
- fever;
- Chills;
- Other signs of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, etc.).
Inflammation of the prostate is accompanied by pain in the perineum, groin area and scrotum.
Pain and rapid urination are also characteristics.Sometimes, in the urine, you will notice the white purulent discharge.
In addition, patients can pay attention to the lack of night and morning erections, poor quality of erections during intimacy, and a sharp shortening of sexual intercourse.
Typical symptoms of urinary disorders occur: weak urine and frequent impulse flow, although the urine itself stands out.
In the future, without treatment, chronic prostatitis will reach a vertical level: a disease of sexual function appears.For example:
- erection or lack of deficiency;
- Painful erection, so the patient escapes sexual intercourse;
- an erased orgasm;
- Short sex;
- The soreness of ejaculation.
Of all prostatitis, chronic abortion prostatitis is 95%, mainly suffering from men around 30 years of age.It is characterized by constant or periodic pain in the pelvis, prostate, scrotum, and in laboratory analysis there are no signs of inflammation.The cause of the disease is certainly not established.
diagnosis
In the diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis, in addition to collecting complaints, dissolution and examination of patients, the following methods are also used:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Microscopy examines the secrets of the prostate and sows them on nutrient medium to detect pathogens (secrets are obtained after prostate finger massage through rectal massage);
- Urine cytology studies;
- Ultrasound of the prostate and pelvic organs;
- Computed tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI);
- Thin urine from urethra smeared.
The differential diagnosis is intended to distinguish between prostatitis, prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, signs of stone in the prostate.
A complete list of diagnostic procedures and medications for treating prostatitis in federal aid standards starting in 2012.
Treatment of prostatitis
The same symptoms may be signs of various diseases, which may not occur according to textbooks.Don't try to be treated with your doctor.Surgeon - Urologists can cause prostatitis.
The purpose of treatments aimed at eliminating the causes of prostatitis is to eliminate pathogens.According to the determined cause, regulations for antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs.During chronic process-4-8 weeks, the duration of acute prostatitis treatment is 7-10 days.
To treat bacterial infections, they are used:
- Antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin);
- macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- doxycycline;
- Antibacterial drugs.
Antifungal (DIFLUCAN, fluconazole) is prescribed in oral and rectal candles.
In addition, other types of therapies are used:
- Anti-allergicity (Suprastin, Claritin, diamine);
- Anti-inflammatory (indomethacin, diclofenac);
- Anesthetics (No-Shpa, Analgin, Baralgin).
They were also appointed:
- physiotherapy;
- Medical gymnastics;
- Prostate massage.
The entire treatment process takes 3-4 months.
prevention
To prevent disease, the following conditions must be observed:
- Regular sex life;
- Reject bad habits;
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, walk in fresh air);
- Follow the diet;
- Visit urologists regularly.